What Is a Residential Property?
As the name suggests, Residential land is any plot, tract or area of land that is purposeful for housing, owner-occupied residing or tenant accommodation. This type of land can be used to construct single-family homes, apartments, multifamily units, studio houses, or other dwellings to qualify as residential property.
Also Read: How To Apply for Land-Use Change
These residential properties are zoned by the local development authority or the Department of Town and country planning for residential land use or for an investment opportunity to generate income in the form of rent.
Different Types of Residential Buildings

Residential land can be widely classified into the following types:
Stand-alone Houses
A stand-alone house is a free-standing residential building, commonly known as a detached residence or detached house, single-family home, or single-detached dwelling.
Multi-family Residential
Multi-family residential buildings or multi-dwelling units (MDUs) is a type of residential property that involves multiple separate houses inside one building, including apartments, row houses, bedsits, condominiums, cluster-house flats, etc.
Mobile Homes
Mobile homes involve park homes, trailers, RVs, caravans, and motorhomes that can be easily moved from one place to another.
Duplexes
These housing types have two separate living units in one structure, with two distinct entrances.
Things to Consider Before Buying Residential Property
If you’re thinking of buying a residential property there are certain things you need to consider before taking the plunge. Below are some essential points:
- Check the developer’s reputation by looking at the projects delivered by him as well as their goodwill in the real estate market.
- The location and neighbourhood of the property are of utmost importance when considering all the amenities and specifications you desire. For instance, consider factors such as ease of accessibility, road conditions, construction quality, recreational activities, and future infrastructure developments in the surrounding vicinity of the property.
- Check connectivity from the major points, including schools, offices, stations, bus stops, and express highways, which adds to the convenience and accessibility.
- Next, the house should be properly ventilated and the living space must be well utilised that fulfil all the family requirements.
- Inspect the quality of the material and the fittings used in the construction of your home.
- If you’re buying an old property, scrutinise the age and condition of the home at the time of purchase, which might impact the cost of repairs and maintenance.
- Make sure there should be enough space for all the compartments of the house, including bedrooms, bathrooms, and kitchens, and the ceiling height should be at least 10-12 feet.
- For maximum return on investment, account the rental and the future resale value. Research the surrounding and proposed developments in the area that will garner a good rental or resale price in the long run.
Benefits of Residential Property

- Purchasing residential land is a more convenient and transparent process as compared to non-residential properties, which require a lot of bureaucratic and legal formalities. Moreover, buying residential flats and apartments is far less time-consuming than other types of property.
- If you’re planning to enter the real estate market, investing in residential property is a better option as it boasts comparatively lower costs and fewer complications than commercial properties.
- Finding tenants for a residential house is a much easier process, as leases can be tailored to the needs of both the homeowner and the tenant.
- The housing sector has shown exponential growth because of the high demand in our country as people buy the property as part of their residential use or investment.
- Maintaining a residential property requires a smaller scale of budget when compared to commercial properties.
Also Read: Factors that Affect the Construction Cost
Non Residential Land
Non-residential meaning a building or structure of any kind whatsoever used, designed or intended to be utilised for non-residential use. This type of land can serve a variety of purposes, from commercial centres, educational institutions, and healthcare facilities, to agricultural land and industrial factories. Depending on the intended use, this land is further classified into different categories.
Industrial Land
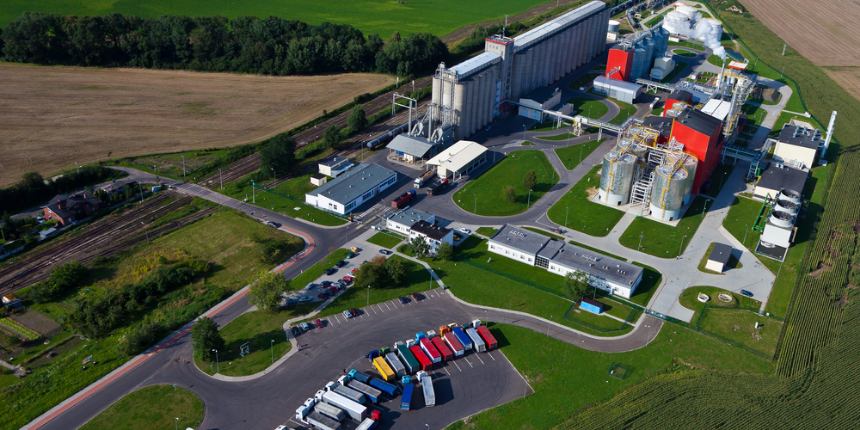

Industrial zoning is a classification of land used for manufacturing or packaging side businesses. Types of buildings in industrially zoned areas include factories, storage facilities, plants and airports. This type of land is a valuable asset for cities and towns, often located on the outskirts of the urban areas. Noise and environmental factors are considered to specifically set aside the industrial-zoned areas to avoid a buffer between businesses and the local population.
Commercial Property

Commercial refers to any property used for business or profit-gaining activities, such as hospitals, assembly plants, storage warehouses, retail stores, shopping centres, office spaces, etc. The sole purpose to purchase the commercial property is to run the business by the owners or rent it out to tenants to generate profit gains. When selecting commercial land, check out developing projects in the area that may influence the value of the land in the near future.
Types of Commercial Property
Office Buildings:
This is one of the most common types of commercial property that involves small professional office buildings, single-tenant buildings, downtown skyscrapers, etc.
Retail Buildings:
This includes grocery stores, small shopping centres, power centres, restaurants, etc.
Multi-Family Buildings:
High-rise apartment buildings, condominiums or complexes occupied generally by the large professional company or MNCs.
Land
A type of undeveloped, or underdeveloped land which will be commercialised in the near future for parks, sports activities or other special amenities.
Miscellaneous
This includes all other commercial buildings including the hospitality sector, self-storage developments, research centres, medical, and many more.
Difference Between Residential and Commercial Property
Below we’ve listed differences between the residential and commercial property based on the multiple factors, functional purposes and requirements.
Formalities in Purchasing-
Residential properties are simpler to buy and require less investment upfront than commercial properties. The commercial property owner undergoes a more thorough investigation and legalities before a purchase is made.
Return Profile-
The return on investment for commercial properties is higher than residential properties benefitting the owners with ROI rates ranging from 6-12% as compared to 4-10% for residential properties.
Risk Profile-
Commercial properties are leased out for longer periods, generally 8-10 years, providing landlords more stability and a bulk of money. However, the notice period for commercial properties is much longer-lasting than for residential properties, making it a higher risk for the tenants to leave the property.
Location-
In construction buildings, location is of prime importance, which might affect the monetary gains. It needs to be in a well-connected area with public transportation and has access to necessary utilities like water supply, waste disposal, etc. Whereas residential property can be in any suitable location as long as it meets the basic needs of the owners.
Loans-
Individual loans are provided for residential properties, while businesses must apply for a commercial land loan. It is a lengthy process that requires numerous documents, formalities and additional maintenance costs, conditions, the loan’s tenure and more.
Law-
Residential legislation generally supports tenants, making it hard for owners to evict them from their property. Conversely, when it comes to commercial land rentals, the situation is more balanced since both parties agree with the contract law.
Cost and Maintenance-
The cost of construction and maintenance for commercial buildings is much higher than for residential buildings. This is due to the cost of materials used, overhead supplies, specialised equipment, and the need for subcontractors, engineers, and skilled labourers.
Agricultural Land

Agricultural land utilised for grazing livestock, cultivating permanent crops, or other farming activities is exclusively open for sale to farmers. It is distinct from urban land which is used for residential or commercial purposes. However, savvy investors must first convert the land from agricultural to non-agricultural property to reap the rewards in the long run.
Conversion of Agricultural Land to Residential
In order to use agricultural land in India for any other purpose like residential, commercial or industrial, the owner must follow a legal process known as land-use conversion. The land-use change is vested in the local authorities- revenue department or planning body. To do this, the owner must submit an application to the authority of the land revenue department along with certified documents:-
- ID proof
- Mutation letter
- Copy of the Sale deed/Gift/Partition deed
- RTC (record of rights, tenancy and crops).
- No-objection certificate
- Land utilisation plan
- Water certificate
- Tax receipt
- Certified land survey map
- Project report (the extent of land, ownership, kind of soil and crops, mortgages and litigations).
In A Nutshell
Choose the right type of land for your needs and make an informed decision by considering various factors such as budget, ownership, financing, property care and management, legalities and regulatory issues, location and market risk involved in these properties. For more information and guidance on how to rent or buy properties, contact the experts at Interior Company.